PersonClassInterfaceCollectionTest
PersonClassInterfaceCollectionTest
OO vs FP
Java9 Immutable Collection
Java9 Immutable Collection
https://dzone.com/articles/immutable-collections-in-java-9
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/9/core/creating-immutable-lists-sets-and-maps.htm#JSCOR-GUID-202D195E-6E18-41F6-90C0-7423B2C9B381
List list3 = List.of("One", "Two", "Three");
Set set3 = Set.of("One", "Two", "Three");
Map map = Map.of("One", "1", "Two", "2", "Three", "3");
Creating Immutable Collection (Java8 or lower)
- Collections.unmodifiableList(list) 사용
- Arrays.asList( … ) 사용
- stream.of(….).collect(collectingAndThen(toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList)) 사용
- Guava 라이브러리 사용
Java Collections: List, Set, Map
Java Collections: List, Set, Map (http://web.mit.edu/6.031/www/sp17/classes/02-basic-java/#java_collections)
A List contains an ordered collection of zero or more objects, where the same object might appear multiple times.
A Set is an unordered collection of zero or more unique objects.
A Map is similar to a dictionary (key, value).
Equals & Contains
import java.util.*;
class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
private static int count = 0; // static (class) field
protected String name; // instance field
protected int age; // instance field
public Person() {
//System.out.println("Person Constructor"); // this("", 0); error: call to this must be first statemenht in constructor
this("", 0);
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
count++;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person(Person other) {
this(other.name, other.age);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void set(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void set(Person other) {
this.name = other.name;
this.age = other.age;
}
public Person clone() {
Person p = new Person(this.name, this.age);
return p;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) { // Object.equals overriding
if (other instanceof Person) {
Person that = (Person) other;
return that.canEqual(this) && this.getName().equals(that.getName()) && this.getAge() == that.getAge();
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return (41 * getName().hashCode() + getAge());
}
public boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return (other instanceof Person);
}
@Override
public String toString() { // Object.toString() overriding
return "Person Name: " + name + " Age: " + age;
}
public void print() { // instance methods
System.out.println("Person Name: " + name + " Age: " + age);
}
public static void printCount() { // static (class) methods
System.out.println("Person Count: " + count);
}
public static int getCount() { // static (class) methods
return count;
}
public static void setCount(int value) { // static (class) methods
count = value;
}
public int compareTo(Person other) {
String thisName = this.getName().toUpperCase();
String otherName = ((Person)other).getName().toUpperCase();
//ascending order
return thisName.compareTo(otherName);
//descending order
//return otherName.compareTo(thisName);
}
public static Comparator<Person> AgeComparator = new Comparator<Person>() {
public int compare(Person p1, Person p2) {
int age1 = p1.getAge();
int age2 = p2.getAge();
//ascending order
return age1 – age2;
//descending order
//return age2 – age1;
}
};
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class Student extends Person {
private static int count = 0; // static (class) field
protected int id;
public Student() {
id = 5208;
}
public Student(String name, int age, int id) {
super(name, age);
this.id = id;
count++;
}
public int getID() {
return id;
}
public void setID(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void set(String name, int age, int id) {
super.set(name, age);
this.id = id;
}
public void set(String name, int age) {
super.set(name, age);
}
public void set(Student other) {
this.set(other.name, other.age, other.id);
}
public void set(Person other) {
if (other instanceof Person)
super.set(other);
else
this.set((Student)other);
}
public Student clone() {
Student s = new Student(this.name, this.age, this.id);
return s;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) { // Object.equals overriding
if (other instanceof Student) {
Student that = (Student) other;
return that.canEqual(this) && this.getName().equals(that.getName()) && this.getAge() == that.getAge() && this.getID() == that.getID();
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return (41 * super.hashCode() + getID());
}
public boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return (other instanceof Student);
}
@Override
public String toString() { // Object.toString() overriding
return "Student Name: " + name + " Age: " + age + " ID: " + id;
}
public void superPrint() {
super.print();
}
public void print() { // Person.print() method overriding
System.out.println("Student Name: " + name + " Age: " + age + " ID: " + id);
}
public static void printCount() { // static (class) methods
System.out.println("Student Count: " + count);
}
public static int getCount() { // static (class) methods
return count;
}
public static void setCount(int value) { // static (class) methods
count = value;
}
public int compareTo(Student other) {
String thisName = this.getName().toUpperCase();
String otherName = ((Student)other).getName().toUpperCase();
//ascending order
return thisName.compareTo(otherName);
//descending order
//return otherName.compareTo(thisName);
}
public static Comparator<Student> AgeComparator = new Comparator<Student>() {
public int compare(Student p1, Student p2) {
int age1 = p1.getAge();
int age2 = p2.getAge();
//ascending order
return age1 – age2;
//descending order
//return age2 – age1;
}
};
public static Comparator<Student> IDComparator = new Comparator<Student>() {
public int compare(Student p1, Student p2) {
int id1 = p1.getID();
int id2 = p2.getID();
//ascending order
return id1 – id2;
//descending order
//return id2 – id1;
}
};
}
class PersonStudentTest {
public static void print(Object[] array) {
for(Object o : array) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Person jason1 = new Person("Jason", 10);
Person jason2 = new Person("Jason", 10);
Person jason3 = jason1;
Person jason4 = new Person("Jason", 20);
if (jason1 == jason2)
System.out.println("jason1 == jason2");
else
System.out.println("jason1 != jason2"); // 동일한 reference를 가리키지 않으므로 jason1 != jason2
if (jason1 == jason3)
System.out.println("jason1 == jason3"); // 동일한 reference이므로 jason1 == jason3
else
System.out.println("jason1 != jason3");
if (jason1.equals(jason4))
System.out.println("jason1 == jason4");
else
System.out.println("jason1 != jason4"); // 동일한 reference를 가리키지 않으므로 jason1 != jason4
if (jason1.equals(jason2))
System.out.println("jason1 equals to jason2"); // 내용이 같으므로 jason1 equals to jason2
else
System.out.println("jason1 is not equal to jason2");
if (jason1.equals(jason3))
System.out.println("jason1 equals to jason3"); // 내용이 같으므로 jason1 equals to jason3
else
System.out.println("jason1 is not equal to jason3");
if (jason1.equals(jason4))
System.out.println("jason1 equals jason4");
else
System.out.println("jason1 is not equal to jason4"); // 내용이 다르므로 jason1 is not equal to jason4
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Student john1 = new Student("John", 10, 100);
Student john2 = new Student("John", 10, 100);
Student john3 = john1;
Student john4 = new Student("John", 20, 100);
if (john1.equals(john2))
System.out.println("john1 equals to john2"); // 내용이 같으므로 john1 equals to john2
else
System.out.println("john1 is not equal to john2");
if (john1.equals(john3))
System.out.println("john1 equals to john3"); // 내용이 같으므로 john1 equals to john3
else
System.out.println("john1 is not equal to john3");
if (john1.equals(john4))
System.out.println("john1 equals to john4");
else
System.out.println("john1 is not equal to john4"); // 내용이 다르므로 john1 is not equal to john4
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Student[] sList = new Student[3];
sList[0] = new Student("Kevin", 0, 222);
sList[1] = new Student("Jason", 1, 333);
sList[2] = new Student("John", 2, 111);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT BY NAME (DEFAULT)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList);
print(sList);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by AGE!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList, Student.AgeComparator);
print(sList);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by ID!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList, Student.IDComparator);
print(sList);
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Student[] sList2 = new Student[3];
sList2[0] = new Student("Kevin", 0, 222);
sList2[1] = new Student("Jason", 1, 333);
sList2[2] = new Student("John", 2, 111);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT BY NAME (anonymous method)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList2, new Comparator<Student>() {
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
return s1.getName().toUpperCase().compareTo(s2.getName().toUpperCase());
}
});
print(sList2);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by AGE (anonymous method)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList2, new Comparator<Student>() {
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
return s1.getAge() – s2.getAge();
}
});
print(sList2);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by ID (anonymous method)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList2, new Comparator<Student>() {
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
return s1.getID() – s2.getID();
}
});
print(sList2);
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Student[] sList3 = sList2;
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT BY NAME (lambda)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList3, (Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
ss1.getName().compareTo(ss2.getName())
);
Arrays.stream(sList3).forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by AGE (lambda)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList3, (Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
Integer.compare(ss1.getAge(), ss2.getAge())
);
Arrays.stream(sList3).forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by ID (lambda)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList3, (Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
Integer.compare(ss1.getID(), ss2.getID())
);
Arrays.stream(sList3).forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
List<Student> sList4 = new ArrayList<Student>();
sList4.add(new Student("Kevin", 0, 222));
sList4.add(new Student("Jason", 1, 333));
sList4.add(new Student("John", 2, 111));
System.out.println("STUDENTLIST SORT BY NAME (lambda)!!!");
sList4.sort((Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
ss1.getName().compareTo(ss2.getName())
);
sList4.forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
System.out.println("STUDENTLIST SORT by AGE (lambda)!!!");
sList4.sort((Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
ss1.getAge() – ss2.getAge()
);
sList4.forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
System.out.println("STUDENTLIST SORT by ID (lambda)!!!");
sList4.sort((Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
ss1.getID() – ss2.getID()
);
sList4.forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
}
}
== vs equal vs hashCode vs contains
CollectionEqualsHashcodeContainsTest (updated)
class CollectionEqualsHashcodeContainsTest{
// getReference
public static String getReference(Object o){
return o.getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode(o));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// primitive type (== 연산자는 값이 같으면 true)
int i = 1000;
int j = 1000;
int k = i;
System.out.println("i == j " + (i == j));
System.out.println("i == k " + (i == k));
System.out.println();
// reference type (reference가 같으면 true)
// WARNING: JVM tries to save memory, when the Integer falls in a range (from -128 to 127). Integer v1 = 100, v2 = 100 v1 == v2
Object o1 = i; // boxing
Object o2 = j; // boxing
Object o3 = o1;
System.out.println(getReference(o1) + " o1=" + o1);
System.out.println(getReference(o2) + " o2=" + o2);
System.out.println(getReference(o3) + " o3=" + o3);
System.out.println("o1 == o2 " + (o1 == o2));
System.out.println("o1 == o3 " + (o1 == o3));
System.out.println("o1 equals o2 " + o1.equals(o2));
System.out.println("o1 equals o3 " + o1.equals(o3));
System.out.println("o1.hashCode() == o2.hashCode() " + (o1.hashCode() == o2.hashCode()));
System.out.println("o1.hashCode() == o3.hashCode() " + (o1.hashCode() == o3.hashCode()));
System.out.println();
// reference type (== 연산자는 reference가 같으면 true)
Person p1 = new Person("P",10);
Person p2 = new Person("P",10);
Person p3 = p1;
System.out.println(getReference(p1) + " p1=" + p1);
System.out.println(getReference(p2) + " p2=" + p2);
System.out.println(getReference(p3) + " p3=" + p3);
System.out.println("p1 == p2 " + (p1 == p2));
System.out.println("p1 == p3 " + (p1 == p3));
System.out.println("p1 equals p2 " + p1.equals(p2));
System.out.println("p1 equals p3 " + p1.equals(p3));
System.out.println("p1.hashCode() == p2.hashCode() " + (p1.hashCode() == p2.hashCode()));
System.out.println("p1.hashCode() == p3.hashCode() " + (p1.hashCode() == p3.hashCode()));
System.out.println();
// String type (== 연산자는 reference가 같으면 true)
String s1 = "PP"; // String literal을 사용할 경우, pool에서 관리
String s2 = "PP"; // String literal을 사용할 경우, pool에서 관리
String s3 = s1;
String s4 = "P" + "P"; // String literal을 사용할 경우, pool에서 관리
String s5 = new String("PP");
String s6 = "PP" + ""; // String literal을 사용할 경우, pool에서 관리
String s7 = s1 + ""; // String + String literal이라서 새로 생성
System.out.println(getReference(s1) + " s1=" + s1);
System.out.println(getReference(s2) + " s2=" + s2);
System.out.println(getReference(s3) + " s3=" + s3);
System.out.println(getReference(s4) + " s4=" + s4);
System.out.println(getReference(s5) + " s5=" + s5);
System.out.println(getReference(s6) + " s6=" + s6);
System.out.println(getReference(s7) + " s7=" + s7);
System.out.println("s1 == s2 " + (s1 == s2));
System.out.println("s1 == s3 " + (s1 == s3));
System.out.println("s1 == s4 " + (s1 == s4));
System.out.println("s1 == s5 " + (s1 == s5));
System.out.println("s1 == s6 " + (s1 == s6));
System.out.println("s1 == s7 " + (s1 == s7));
System.out.println("s1 equals s2 " + s1.equals(s2));
System.out.println("s1 equals s3 " + s1.equals(s3));
System.out.println("s1 equals s4 " + s1.equals(s4));
System.out.println("s1 equals s5 " + s1.equals(s5));
System.out.println("s1 equals s6 " + s1.equals(s6));
System.out.println("s1 equals s7 " + s1.equals(s7));
System.out.println("s1.hashCode() == s2.hashCode() " + (s1.hashCode() == s2.hashCode()));
System.out.println("s1.hashCode() == s3.hashCode() " + (s1.hashCode() == s3.hashCode()));
System.out.println("s1.hashCode() == s4.hashCode() " + (s1.hashCode() == s4.hashCode()));
System.out.println("s1.hashCode() == s5.hashCode() " + (s1.hashCode() == s5.hashCode()));
System.out.println("s1.hashCode() == s6.hashCode() " + (s1.hashCode() == s6.hashCode()));
System.out.println("s1.hashCode() == s7.hashCode() " + (s1.hashCode() == s7.hashCode()));
System.out.println();
// ArrayList
System.out.println("pList");
List<Person> pList = new ArrayList<Person>();
pList.add(p1);
pList.add(p2);
pList.add(p3);
pList.forEach((p) -> System.out.println(p));
System.out.println("pList contains p1: " + pList.contains(p1));
System.out.println("pList contains p2: " + pList.contains(p2));
System.out.println("pList contains p3: " + pList.contains(p3));
System.out.println("pList contains new Person: " + pList.contains(new Person("P",10)));
System.out.println();
// HashSet의 경우 hashCode가 일치하면 동일한 것으로 간주하여 replace함
System.out.println("pSet");
Set<Person> pSet = new HashSet();
pSet.add(p1);
pSet.add(p2);
pSet.add(p3);
pSet.forEach((p) -> System.out.println(p));
System.out.println("pSet contains p1: " + pSet.contains(p1));
System.out.println("pSet contains p2: " + pSet.contains(p2));
System.out.println("pSet contains p3: " + pSet.contains(p3));
System.out.println("pSet contains new Person: " + pSet.contains(new Person("P",10)));
System.out.println();
// HashMap의 경우 key 값은 hashCode가 일치하면 동일한 것으로 간주하여 replace함
System.out.println("pMap");
Map<Person, Integer> pMap = new HashMap<Person, Integer>();
pMap.put(p1, 1);
pMap.put(p2, 2);
pMap.put(p3, 3);
pMap.forEach((p, e) -> System.out.println(p + " " + e));
System.out.println("pMap contains p1: " + pMap.containsKey(p1));
System.out.println("pMap contains p2: " + pMap.containsKey(p2));
System.out.println("pMap contains p3: " + pMap.containsKey(p3));
System.out.println("pMap contains new Person: " + pMap.containsKey(new Person("P",10)));
System.out.println();
// Array
System.out.println("pArray");
Person[] pArray = new Person[3];
pArray[0] = p1;
pArray[1] = p2;
pArray[2] = p3;
Arrays.asList(pArray).forEach(p -> System.out.println(p));
System.out.println("pArray contains p1: " + Arrays.asList(pArray).contains(p1));
System.out.println("pArray contains p2: " + Arrays.asList(pArray).contains(p2));
System.out.println("pArray contains p3: " + Arrays.asList(pArray).contains(p3));
System.out.println("pArray contains new Person: " + Arrays.asList(pArray).contains(new Person("P",10)));
System.out.println();
}
}
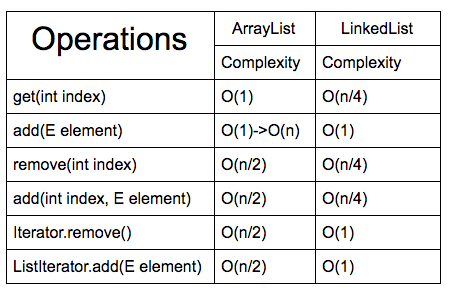
ArrayList vs LinkedList
Difference between Array and ArrayList
- Resizable
- Array is static in size that is fixed length data structure, One can not change the length after creating the Array object.
- ArrayList is dynamic in size. Each ArrayList object has instance variable capacity which indicates the size of the ArrayList. Its capacity grows automatically.
- Primitives
- Array can contain both primitive data types (e.g. int, float, double) as well as objects.
- ArrayList can not contains primitive data types it can only contains objects.
- Adding elements
- In array we insert elements using the assignment(=) operator.
- We can insert elements into the ArrayList using the add() method
- Length
- Each array object has the length variable which returns the length of the array.
- Length of the ArrayList is provided by the size() method.
// Array
int[] integerArray = new int[3];
integerArray[0] = 1;
integerArray[1] = 2;
integerArray[2] = 3;
for (int i : integerArray) System.out.println(i);
for (int j=0; j<integerArray.length; j++) System.out.println(integerArray[ j ]);
int k = 0;
while (k < integerArray.length) System.out.println(integerArray[k++]);
// ArrayList
ArrayList integerList = new ArrayList();
integerList.add(1); //cannot store primitive in ArrayList, instead autoboxing will convert int to Integer object
integerList.add(2); //cannot store primitive in ArrayList, instead autoboxing will convert int to Integer object
integerList.add(3); //cannot store primitive in ArrayList, instead autoboxing will convert int to Integer object
for (int m : integerList) System.out.println(m);
for (int n=0; n<integerList.size(); n++) System.out.println(integerList.get(n));
Iterator itr = integerList.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) System.out.println(itr.next());
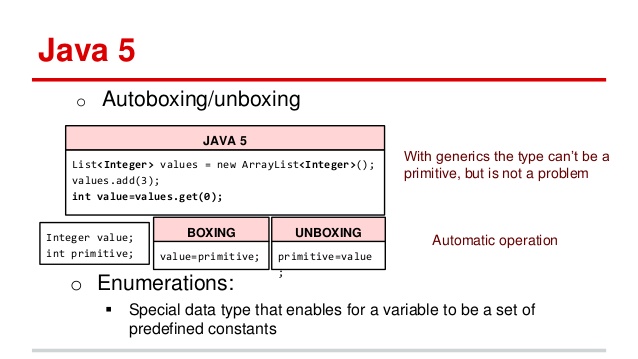
Autoboxing and Unboxing (Java1.5)
lecture8
lecture8