// break a loop if 'q'-key is pressed
static Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
public static boolean getUserInputExitKey() {
System.out.println("Please enter key to continue or the q-key to exit.");
String input = scan.nextLine();
if (input == null || input.contentEquals("")) return false;
if (input.contentEquals("q")) return true;
else return false;
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
do {
// do whatever..
} while(!getUserInputExitKey());
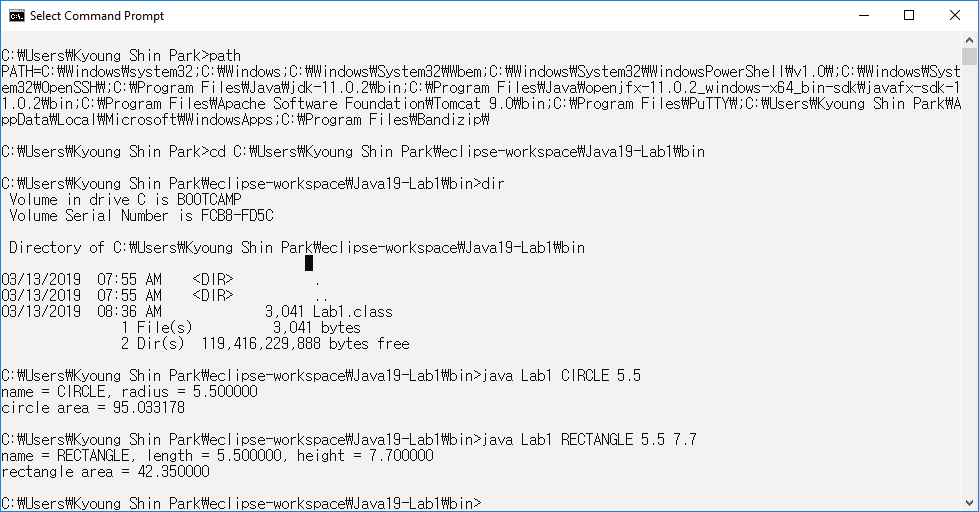
List of DOS commands
How to use the Windows command line (DOS)
https://www.computerhope.com/issues/chusedos.htm
List of DOS commands (on Windows Command Prompt)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_DOS_commands
cd – change directory
cls – clear screen
dir – directory
path – displays a path for executable files
returning an array from a method vs passing an array as parameter to a method
// returning an array from a method vs passing an array as parameter to a method
// passing an array as parameter to a method
public static int sumArray(int[] arr) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
return sum;
}
// returning an array from a method
public static int[] assignArray(int length) {
int[] arr = new int[length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = i;
}
return arr;
}
////////////////////////////////////// in main
// returning an array from a method
int[] arr1 = assignArray(3);
int[] arr2 = assignArray(5);
for (int e : arr1) System.out.println(e); // 0 1 2
for (int e : arr2) System.out.println(e); // 0 1 2 3 4
// passing an array as parameter to a method
int[] array1 = {100, 200, 300};
int[] array2 = {50, 60, 70, 80, 90};
int sum1 = sumArray(array1);
int sum2 = sumArray(array2);
System.out.println("array1 sum=" + sum1); // 100 + 200 + 300 = 600
System.out.println("array2 sum=" + sum2); // 50 + 60 + 70 + 80 + 90 = 350
2D Array
// 2D array
char[] ops = {'+', '-', '*', '/'};
int[][] numbers = {{60,50}, {40,30}, {20,10}};
for (char op : ops) {
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
int result = calc(numbers[i][0], numbers[i][1], op);
System.out.printf("result = %d %s %d = %d\n", numbers[i][0], op, numbers[i][1], result);
}
}result = 60 + 50 = 110
result = 40 + 30 = 70
result = 20 + 10 = 30
result = 60 – 50 = 10
result = 40 – 30 = 10
result = 20 – 10 = 10
result = 60 * 50 = 3000
result = 40 * 30 = 1200
result = 20 * 10 = 200
result = 60 / 50 = 1
result = 40 / 30 = 1
result = 20 / 10 = 2
Person Array
Person[] pArray = new Person[5];
// 만약 Person 객체를 하나만 생성한 후 for문에서 공유해 사용할 경우
// 마지막으로 입력된 데이터로 모든 데이터값이 치환됨
Person p = new Person();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.print("\n\nEnter Person name : ");
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
p.setName(input.nextLine()); // 입력정보
System.out.print("\n\nEnter Person age [int] : ");
p.setAge(input.nextInt()); // 입력정보
p.print();
pArray[i] = p; // 리스트에 들어간 모든 원소는 동일한 p
}
System.out.println("pArray : " + Arrays.toString(pArray));
Person[] pArray = new Person[5];
// 아래와 같이 for문 안에 Person p = new Person()와같이
// 새로운 객체를 생성해야 각자 다르게 입력된 정보가 들어가게 됨
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Person p = new Person();
System.out.print("\n\nEnter Person name : ");
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
p.setName(input.nextLine()); // 입력정보
System.out.print("\n\nEnter Person age [int] : ");
p.setAge(input.nextInt()); // 입력정보
p.print();
pArray[i] = p; // 이때 p는 새로운 Person객체
}
System.out.println("pArray2 : " + Arrays.toString(pArray2));
Integer Array
int[] integerArray = new int[3];
integerArray[0] = 1;
integerArray[1] = 2;
integerArray[2] = 3;
for (int i : integerArray)
System.out.println(i);
for (int j = 0; j < integerArray.length; j++)
System.out.println(integerArray[ j ]);
int k = 0;
while (k < integerArray.length)
System.out.println(integerArray[k++]);
// int array
// 만약 int value1를 for문에서 공유해 사용한다해도
// intArray1[i]에 값이 들어가므로 각각 다른 입력값이 들어가게 됨
int value1 = 0;
int[] intArray1 = new int[3];
for (int i = 0; i < intArray1.length; i++) {
System.out.print("Please enter int number: ");
value1 = scan.nextInt(); // 10 20 30
intArray1[i] = value1;
}
for (int v : intArray1) System.out.println(v); // 10 20 30
// int value2를 for문에서 내부에서 매번 생성해서 사용한다해도
// intArray2[i]에 값이 들어가므로 각각 다른 입력값이 들어가게 됨
int[] intArray2 = new int[3];
for (int i = 0; i < intArray1.length; i++) {
System.out.print("Please enter int number: ");
int value2 = scan.nextInt(); // 100 200 300
intArray2[i] = value2;
}
for (int v : intArray2) System.out.println(v); // 100 200 300
Control Statement
import java.util.Scanner;
// for, foreach, if/else-if, switch, array, 2D array
public class BasicCalculation {
public static Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
// calc (using if/else-if)
public static int calc(int x, int y, char op) {
if (op == '+') return x + y;
else if (op == '-') return x - y;
else if (op == '*') return x * y;
else if (op == '/') return x / y;
else {
System.out.println("op not found");
return 0;
}
}
// calc2 (using switch)
public static int calc2(int x, int y, char op) {
switch(op) {
case '+': return x + y;
case '-': return x - y;
case '*': return x * y;
case '/': return x / y;
default:
System.out.println("op not found");
return 0;
}
}
// get user input op[+,-,*,/]
static public char getUserInputOp() {
char value = '\0';
do {
System.out.printf("Please enter the operator [+,-,*,/]: ");
try {
value = scan.next().charAt(0);
System.out.println("value=" + value);
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.printf("Error! Please re-enter!\n");
scan.next();
continue;
}
} while (value != '+' && value != '-' && value != '*' && value != '/');
return value;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// for
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("i=" + i);
}
// while
int j = 0;
while (j < 5) {
System.out.println("j=" + j);
j++;
}
// do-while
int k = 0;
do {
System.out.println("k=" + k);
k++;
} while (k < 5);
// break (0~4)
int x = 0;
while (true) {
if (x >= 5) break;
System.out.println("x=" + x);
x++;
}
// continue (0~4)
int y = 0;
while (y < 5) {
y++; // (1~5)
if (y % 2 == 1) // 홀수
continue;
System.out.println("y=" + y); // 짝수만 출력
}
// for-each
System.out.print("Please enter two numbers: ");
x = scan.nextInt();
y = scan.nextInt();
char[] ops = {'+', '-', '*', '/', '^'}; // char array
for (char op : ops) {
int z = calc(x, y, op);
System.out.printf("z = %d %s %d = %d\n", x, op, y, z);
}
// 2D array
int[][] numbers = {{49, 57}, {36, 29}, {88, 66}};
for (char op: ops) {
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
int r = calc2(numbers[i][0], numbers[i][1], op);
System.out.printf("r = %d %c %d = %d\n",
numbers[i][0], op, numbers[i][1], r);
}
}
// user input
System.out.print("Please enter two numbers: ");
x = scan.nextInt();
y = scan.nextInt();
char op = getUserInputOp();
int w = calc2(x, y, op);
System.out.printf("w = %d %s %d = %d\n", x, op, y, w)
}
}lab1
Lab1
java1-lab1
Lab1 프로젝트 디렉토리 안에 모든 파일(src/*.java & bin/*.class)와 보고서(3-4장정도 – 장수제한없음)를 넣고 Lab1_학번_이름.zip 압축한 후 e-learning(http://lms.dankook.ac.kr/index.jsp)으로 제출
1 – method
2 – command line arguments
3 – Scanner 클래스를 이용하여 사용자 입력을 받아서 도형의 면적 계산을 출력한다.
4 – 본인이 원하는 코드를 추가작성한다
1,2,3,4에 해당하는 부분을 /* 주석문 */으로 표시해준다.
Postfix vs Prefix Increment/Decrement Operator
int i = 10;
System.out.println(“i++=” + (i++)); // prints 10 and then increments
System.out.println(“i=” + i); // prints 11
int j = 20;
System.out.println(“++j=” + (++j)); // increments and then prints 21
System.out.println(“j=” + j); // prints 21
Operator Precedence
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/nutsandbolts/operators.html
| Operators | Precedence |
|---|---|
| postfix | expr++ expr-- |
| unary | ++expr --expr +expr -expr ~ ! |
| multiplicative | * / % |
| additive | + - |
| shift | << >> >>> |
| relational | < > <= >= instanceof |
| equality | == != |
| bitwise AND | & |
| bitwise exclusive OR | ^ |
| bitwise inclusive OR | | |
| logical AND | && |
| logical OR | || |
| ternary | ? : |
| assignment | = += -= *= /= %= &= ^= |= <<= >>= >>>= |
