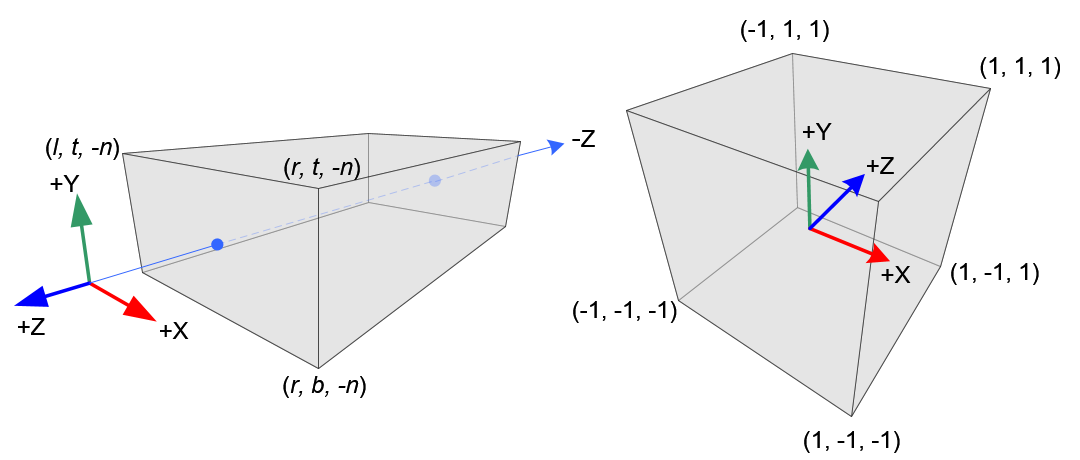
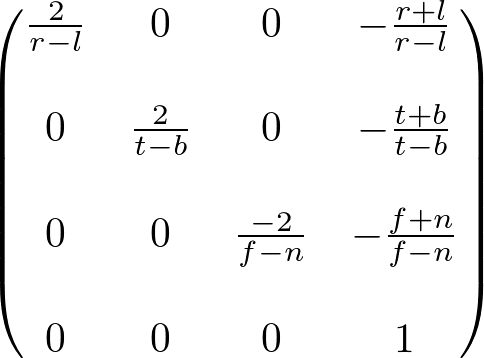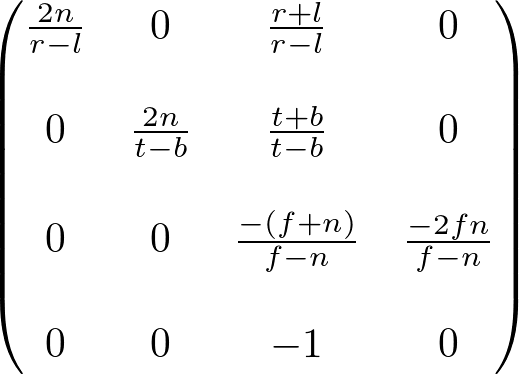void mprint(glm::mat4 Mat)
{
printf(“\n %f %f %f %f\n %f %f %f %f\n %f %f %f %f\n %f %f %f %f\n\n”,
Mat[0][0], Mat[1][0], Mat[2][0], Mat[3][0],
Mat[0][1], Mat[1][1], Mat[2][1], Mat[3][1],
Mat[0][2], Mat[1][2], Mat[2][2], Mat[3][2],
Mat[0][3], Mat[1][3], Mat[2][3], Mat[3][3]);
}
float theta(const glm::vec3 &v1, const glm::vec3 &v2)
{
float len1 = (float)sqrtf(v1[0]*v1[0] + v1[1]*v1[1] + v1[2]*v1[2]);
float len2 = (float)sqrtf(v2[0]*v2[0] + v2[1]*v2[1] + v2[2]*v2[2]);
return (float)acosf(dot(v1, v2)/len1*len2);
}
glm::vec3 computeNormal(glm::vec3& a, glm::vec3& b, glm::vec3& c)
{
glm::vec3 normal = glm::normalize(glm::cross(c – a, b – a));
return normal;
}
void vec3Test()
{
const float v[3] = { 1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f };
vec3 a(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), b(1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f), c(b);
vec3 d = c;
vec3 e = c;
vec3 f = a;
cout << “a = ” << a[0] << ” ” << a[1] << ” ” << a[2] << endl;
cout << “b = ” << b[0] << ” ” << b[1] << ” ” << b[2] << endl;
cout << “c = ” << c[0] << ” ” << c[1] << ” ” << c[2] << endl;
cout << “d = ” << d[0] << ” ” << d[1] << ” ” << d[2] << endl;
cout << “e = ” << e[0] << ” ” << e[1] << ” ” << e[2] << endl;
a[0] = 4;
a[1] = 5;
a[2] = 6;
cout << “after assignments, a (4,5,6) ” << endl;
cout << “a = ” << a[0] << ” ” << a[1] << ” ” << a[2] << endl;
cout << “b = ” << b[0] << ” ” << b[1] << ” ” << b[2] << endl;
cout << “Unary Operation” << endl;
a += b;
cout << “a += b ” << endl;
cout << “a = ” << a[0] << ” ” << a[1] << ” ” << a[2] << endl;
a -= b;
cout << “a -= b ” << endl;
cout << “a = ” << a[0] << ” ” << a[1] << ” ” << a[2] << endl;
a *= 1.5;
cout << “a *= 1.5 ” << endl;
cout << “a = ” << a[0] << ” ” << a[1] << ” ” << a[2] << endl;
a /= 1.5;
cout << “a /= 1.5 ” << endl;
cout << “a = ” << a[0] << ” ” << a[1] << ” ” << a[2] << endl;
cout << “Binary Operation” << endl;
c = a + b;
cout << “c = a + b -> c ” << endl;
cout << “c = ” << c[0] << ” ” << c[1] << ” ” << c[2] << endl;
c = a – b;
cout << “c = a – b -> c ” << endl;
cout << “c = ” << c[0] << ” ” << c[1] << ” ” << c[2] << endl;
cout << “a == b” << endl;
if (a == b)
cout << ” is true” << endl;
else
cout << ” is false” << endl;
cout << “b == d” << endl;
if (b == d)
cout << ” is true” << endl;
else
cout << ” is false” << endl;
// magnitude
cout << “a = ” << a[0] << ” ” << a[1] << ” ” << a[2] << endl;
cout << “b = ” << b[0] << ” ” << b[1] << ” ” << b[2] << endl;
cout << “a magnitude = ” << (float)sqrt(a[0]*a[0] + a[1]*a[1] + a[2]*a[2]) << endl;
cout << “b magnitude = ” << (float)sqrt(b[0]*b[0] + b[1]*b[1] + b[2]*b[2]) << endl;
// normalize
c = normalize(a);
cout << “c = normalize(a) = ” << c[0] << ” ” << c[1] << ” ” << c[2] << endl;
cout << “c magnitude = ” << (float)sqrt(c[0]*c[0] + c[1]*c[1] + c[2]*c[2]) << endl;
d = normalize(b);
cout << “d = normalize(b) = ” << d[0] << ” ” << d[1] << ” ” << d[2] << endl;
cout << “d magnitude = ” << (float)sqrt(d[0]*d[0] + d[1]*d[1] + d[2]*d[2]) << endl;
// dot product, theta, cross product, compute normal
cout << “dot(a, b) = ” << dot(a, b) << endl;
cout << “a,b angle = ” << degrees(theta(a, b)) << endl;
e = cross(a, b);
cout << “e = cross(a, b) = ” << e[0] << ” ” << e[1] << ” ” << e[2] << endl;
f = cross(vec3(1.0f, 3.0f, -4.0f), vec3(2.0f, -5.0f, 8.0f));
cout << “(1, 3, -4) x (2, -5, 8) = ” << f[0] << ” ” << f[1] << ” ” << f[2] << endl;
glm::vec3 g = computeNormal(glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f));
cout << “g = ” << g[0] << ” ” << g[1] << ” ” << g[2] << endl;
}
void mat4Test()
{
// matrix test
glm::mat4 A(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // column1
0.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // column2
0.0f, 0.0f, 4.0f, 0.0f, // column3
1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f, 1.0f); // column4
cout << “A = ” << endl;
mprint(A);
glm::mat4 B(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // column1
0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // column2
0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // column3
2.0f, 2.0f, 2.0f, 1.0f); // column4
cout << “B = ” << endl;
mprint(B);
glm::mat4 C = A * B; // multiplication
cout << “C = A*B = ” << endl;
mprint(C);
glm::mat4 D = B * A; // multiplication
cout << “D = B*A = ” << endl;
mprint(D);
glm::mat4 E = glm::inverse(A); // inverse
cout << “E = inverse(A) = ” << endl;
mprint(E);
glm::mat4 I = A * E; // multiplication
cout << “I = A*E = ” << endl;
mprint(I);
glm::vec4 p = glm::vec4(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
glm::vec4 q = A * p;
glm::vec4 r = B * p;
glm::vec4 s = C * p;
glm::vec4 t = D * p;
cout << “q = A*p = ” << endl;
printf(“(1, 0, 0, 1) => (%f, %f, %f, %f)\n”, q[0], q[1], q[2], q[3]);
cout << “r = B*p = ” << endl;
printf(“(1, 0, 0, 1) => (%f, %f, %f, %f)\n”, r[0], r[1], r[2], r[3]);
cout << “s = A*B*p = ” << endl;
printf(“(1, 0, 0, 1) => (%f, %f, %f, %f)\n”, s[0], s[1], s[2], s[3]);
cout << “t = B*A*p = ” << endl;
printf(“(1, 0, 0, 1) => (%f, %f, %f, %f)\n”, t[0], t[1], t[2], t[3]);
glm::mat4 Tx, Ty, Tz;
Tx = glm::translate(glm::mat4(1.0f), glm::vec3(2.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)); // RHS x+ right
Ty = glm::translate(glm::mat4(1.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f)); // RHS y+ up
Tz = glm::translate(glm::mat4(1.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 2.0f)); // RHS z+ front
printf(“Tx\n”);
mprint(Tx);
glm::vec4 Position = glm::vec4(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
glm::vec4 tV = Tx * Position;
printf(“(1, 0, 0, 1) => (%f, %f, %f, %f)\n”, tV[0], tV[1], tV[2], tV[3]);
glm::mat4 Rx, Ry, Rz, Ra;
Rx = glm::rotate(glm::mat4(1.0f), 30.0f, glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
Ry = glm::rotate(glm::mat4(1.0f), 60.0f, glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f));
Rz = glm::rotate(glm::mat4(1.0f), 45.0f, glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f));
Ra = glm::rotate(glm::mat4(1.0f), 45.0f, glm::vec3(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f));
printf(“R\n”);
mprint(Rx);
mprint(Ry);
mprint(Rz);
mprint(Ra);
glm::vec4 tV1 = Ra * Position;
printf(“Ra * Position(1, 0, 0, 1) => (%f, %f, %f, %f)\n”, tV1[0], tV1[1], tV1[2], tV1[3]);
glm::mat4 Sx, Sy, Sz;
Sx = glm::scale(glm::mat4(1.0f), glm::vec3(2, 1, 1));
Sy = glm::scale(glm::mat4(1.0f), glm::vec3(1, 2, 1));
Sz = glm::scale(glm::mat4(1.0f), glm::vec3(1, 1, 2));
printf(“Sy\n”);
mprint(Sy);
glm::vec4 tV2 = Sy * Position;
printf(“(1, 0, 0, 1) => (%f, %f, %f, %f)\n”, tV2[0], tV2[1], tV2[2], tV2[3]);
glm::mat4 TR = Tx * Rz; // Rotate Z and then Translate X
printf(“TR\n”);
mprint(TR);
glm::vec4 tV3 = TR * Position;
printf(“(1, 0, 0, 1) => (%f, %f, %f, %f)\n”, tV3[0], tV3[1], tV3[2], tV3[3]);
mat4 RT = Rz * Tx; // Translate X and then Rotate Z
printf(“RT\n”);
mprint(RT);
glm::vec4 tV4 = RT * Position;
printf(“(1, 0, 0, 1) => (%f, %f, %f, %f)\n”, tV4[0], tV4[1], tV4[2], tV4[3]);
}