Lab4-GeometryPositionColorComposeAnimation (“사” using Parallelepiped & geometry keyframe animation using Catmull-Rom Curve Animation)
lab4-GeometryPositionColorComposeAnimation
Sa::Sa(glm::vec3 p_) : GeometryPositionColor()
{
p = p_;
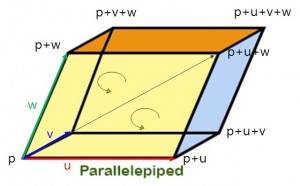
for (int i=0; i<4; i++) pipe[i] = Parallelepiped();
init();
// keyframe animation
std::vector<KeyFrame> keyframes;
keyframes.push_back(KeyFrame(glm::vec3(0, 0, 0), 0));
keyframes.push_back(KeyFrame(glm::vec3(1, 1, 0), 2000));
keyframes.push_back(KeyFrame(glm::vec3(-1, 2, 0), 4000));
keyframes.push_back(KeyFrame(glm::vec3(2, 3, 0), 6000));
setKeyframeAnimation(keyframes);
}
void Sa::init() // “사”
{
glm::vec3 p0 = p;
pipe[0].set(p0, glm::vec3(0.3f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.3f), glm::vec3(0.7f, 1.0f, 0.0f)); // ‘ㅅ’의 첫번 째 획
glm::vec3 p1 = p + glm::vec3(1.4f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
pipe[1].set(p1, glm::vec3(0.3f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.3f), glm::vec3(-0.7f, 1.0f, 0.0f)); // ‘ㅅ’의 두번 째 획
glm::vec3 p2 = p + glm::vec3(2.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
pipe[2].set(p2, glm::vec3(0.3f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.3f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f)); // ‘ㅏ’의 첫번 째 획
glm::vec3 p3 = p + glm::vec3(2.3f, 0.35f, 0.0f);
pipe[3].set(p3, glm::vec3(0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.3f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.3f, 0.0f)); // ‘ㅏ’의 두번 째 획
void Sa::draw(bool wireframe)
{
for (int i=0; i<4; i++) pipe[i].draw();
}
bool Sa::update(float elapsedTime)
{
if (active)
{
if (curve)
{
curve->updatePosition(elapsedTime);
p = curve->getPosition();
// if time is greater than duration, then set time to duration and set active to false
if (!curve->getLoop() && elapsedTime >= curve->getDuration())
{
done = true;
active = false;
}
}
init();
}
return true;
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void GeometryPositionColor::setKeyframeAnimation(std::vector<KeyFrame> frames_)
{
curve = new CatmullRomCurveAnimation(frames_, true);
init();
}