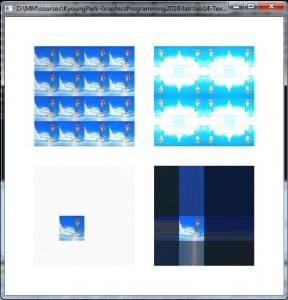
Billboarding & AlphaBlendTextures
lab16-BillboardingTextureShadedQuad
// create a axis-aligned billboard matrix
void buildAxisAlignedBillboardMatrix(glm::mat4& m, glm::vec3& axis)
{
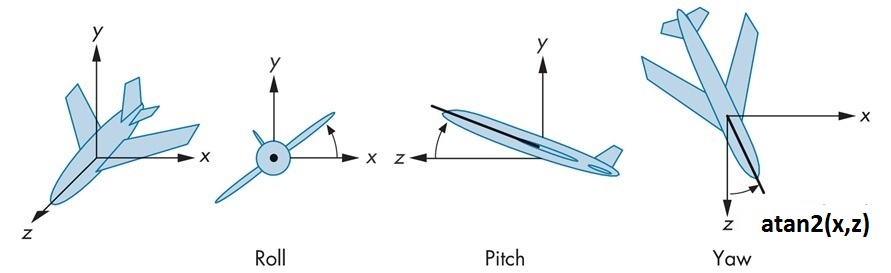
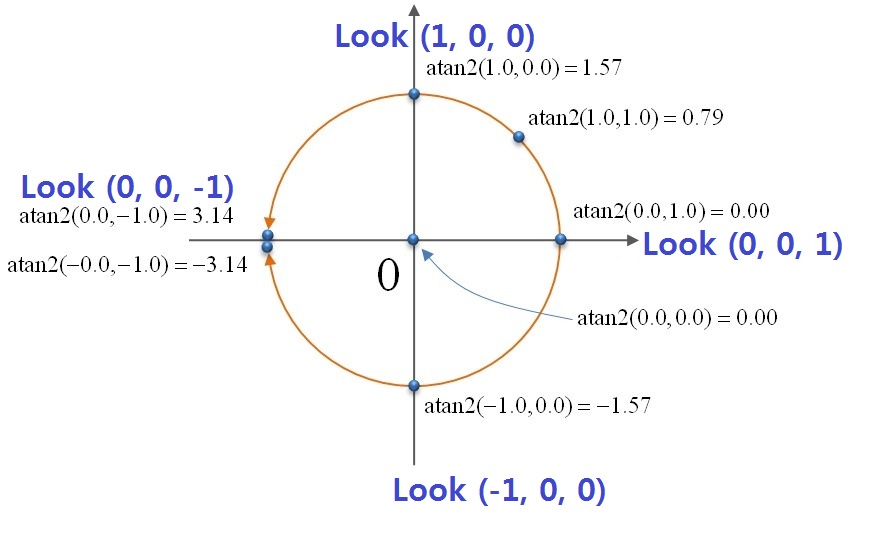
// calculate “-yaw” angle from View matrix (Look.x, Look.z)
float theta = -atan2f(m[0][2], m[2][2]);
float ct = cosf(theta);
float st = sinf(theta);
// normalize
axis = glm::normalize(axis);
// clear out the view matrix passed in
m = glm::mat4(1.0f);
//———————————————
// R = uu’ + cos(theta)*(I-uu’) + sin(theta)*S
//
// S = 0 -z y u’ = (x, y, z)
// z 0 -x
// -y x 0
//———————————————
// calculate “Rotation” matrix using “axis” & “theta”
m[0][0] = axis[0] * axis[0] + ct*(1 – axis[0] * axis[0]) ;
m[0][1] = axis[0] * axis[1] + ct*(0 – axis[0] * axis[1]) + st*(-axis[2]);
m[0][2] = axis[0] * axis[2] + ct*(0 – axis[0] * axis[2]) + st*axis[1];
m[1][0] = axis[1] * axis[0] + ct*(0 – axis[1] * axis[0]) + st*axis[2];
m[1][1] = axis[1] * axis[1] + ct*(1 – axis[1] * axis[1]) ;
m[1][2] = axis[1] * axis[2] + ct*(0 – axis[1] * axis[2]) + st*(-axis[0]);
m[2][0] = axis[2] * axis[0] + ct*(0 – axis[2] * axis[0]) + st*(-axis[1]);
m[2][1] = axis[2] * axis[1] + ct*(0 – axis[2] * axis[1]) + st*axis[0];
m[2][2] = axis[2] * axis[2] + ct*(1 – axis[2] * axis[2]) ;
}
Billboard가 활성화가 되지 않은 상태 (카메라의 시점이 회전된 상태에 따라 알파텍스쳐 나무가 원래 위치한대로 그대로 유지함)

Billboard가 활성화된 상태 (카메라의 시점이 회전된 상태라 해도 알파텍스쳐 나무가 내 시점을 향하여 바라보는 상태를 유지함)