lecture9
lecture8
lecture8
gimbal lock
Euler vs Quaternion
How to Rotate in Unity
Euler Rotation in Unity
// Create a Ra matrix Euler(30, 60, 45)
Matrix4x4 ra = Matrix4x4.Rotate(Quaternion.Euler(30, 60, 45));
// Create a Rb matrix rz -> rx -> ry
Matrix4x4 rz = Matrix4x4.Rotate(Quaternion.Euler(0, 0, 45));
Matrix4x4 rx = Matrix4x4.Rotate(Quaternion.Euler(30, 0, 0));
Matrix4x4 ry = Matrix4x4.Rotate(Quaternion.Euler(0, 60, 0));
Matrix4x4 rb = ry * rx * rz; // Z → X → Y
// ra == rb
// Create a Rc matrix ry -> rx -> rz
Matrix4x4 rc = rz * rx * ry; // Y → X → Z
// rb != rc
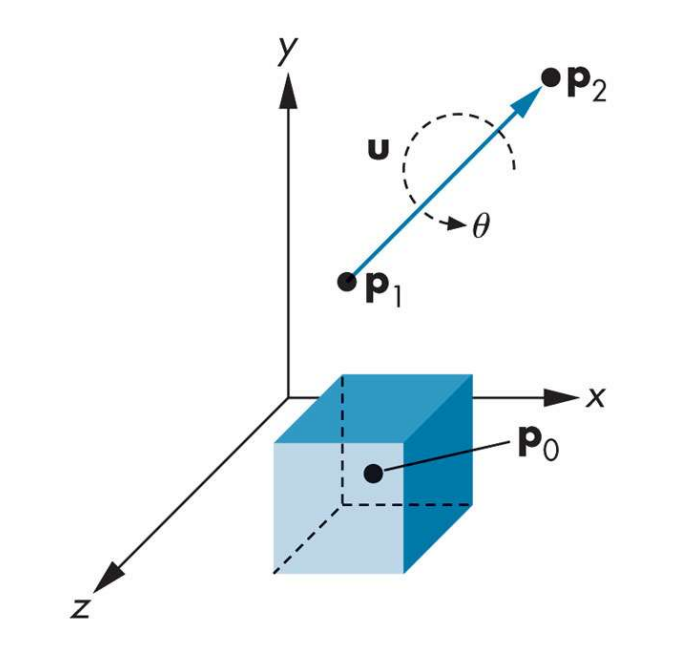
Rotate a point about an arbitrary axis
Rotate a point about an arbitrary axis (3 dimensions)
Written by Paul Bourke
https://paulbourke.net/geometry/rotate/
/*
Rotate a point p by angle around an arbitrary line segment p1-p2
Return the rotated point.
Positive angles are anticlockwise looking down the axis
towards the origin. Assume right hand coordinate system.
*/
public static Vector3 ArbitraryRotate(Vector3 p, float angle, Vector3 p1, Vector3 p2)
{
Vector3 u, q1, q2, q3, q4, q5, q6, q7;
float d;
// (1) translate space so that the rotation axis passes through the origin
q1 = p – p1;
// (2) rotate space about the x axis so that the rotation axis lies in the xz plane
u = p2 – p1; // rotation-axis vector
u = Vector3.Normalize(u);
d = Mathf.Sqrt(u.y*u.y + u.z*u.z);
if (d != 0) {
q2.x = q1.x;
q2.y = q1.y * u.z / d – q1.z * u.y / d;
q2.z = q1.y * u.y / d + q1.z * u.z / d;
} else {
q2 = q1;
}
// (3) rotate space about the y axis so that the rotation axis lies along the z axis
q3.x = q2.x * d – q2.z * u.x;
q3.y = q2.y;
q3.z = q2.x * u.x + q2.z * d;
// (4) perform the desired rotation by theta about the z axis
float theta = Mathf.Deg2Rad * angle;
q4.x = q3.x * Mathf.Cos(theta) – q3.y * Mathf.Sin(theta);
q4.y = q3.x * Mathf.Sin(theta) + q3.y * Mathf.Cos(theta);
q4.z = q3.z;
// (5) apply the inverse of step (3)
q5.x = q4.x * d + q4.z * u.x;
q5.y = q4.y;
q5.z = -q4.x * u.x + q4.z * d;
// (6) apply the inverse of step (2)
if (d != 0) {
q6.x = q5.x;
q6.y = q5.y * u.z / d + q5.z * u.y / d;
q6.z = -q5.y * u.y / d + q5.z * u.z / d;
} else {
q6 = q5;
}
// (7) apply the inverse of step (1)
q7 = q6 + p1;
return q7;
}
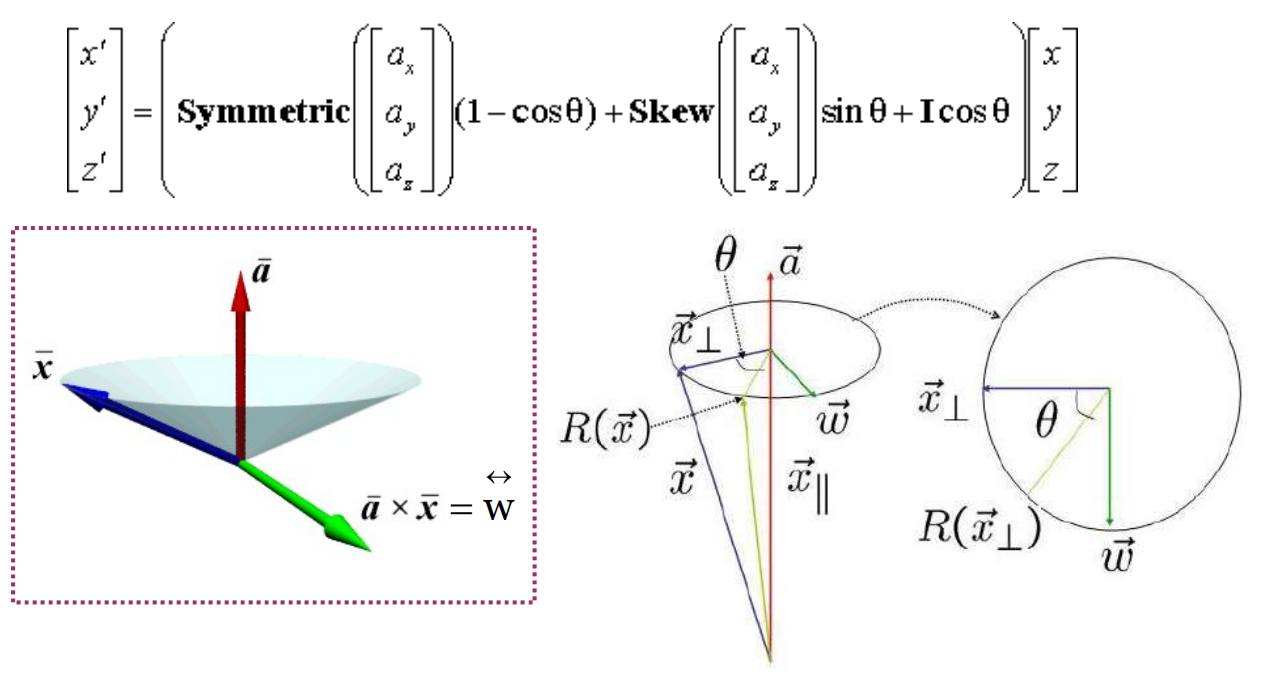
/*
Rotate a point p by angle around an arbitrary axis
Return the rotated point.
Positive angles are anticlockwise looking down the axis
towards the origin. Assume right hand coordinate system.
*/
public static Vector3 ArbitraryRotate(Vector3 p, float angle, Vector3 axis)
{
Vector3 q = Vector3.zero;
float costheta, sintheta;
float theta = Mathf.Deg2Rad * angle;
axis = Vector3.Normalize(axis);
costheta = Mathf.Cos(theta);
sintheta = Mathf.Sin(theta);
q.x += (costheta + (1 – costheta) * axis.x * axis.x) * p.x;
q.x += ((1 – costheta) * axis.x * axis.y – axis.z * sintheta) * p.y;
q.x += ((1 – costheta) * axis.x * axis.z + axis.y * sintheta) * p.z;
q.y += ((1 – costheta) * axis.x * axis.y + axis.z * sintheta) * p.x;
q.y += (costheta + (1 – costheta) * axis.y * axis.y) * p.y;
q.y += ((1 – costheta) * axis.y * axis.z – axis.x * sintheta) * p.z;
q.z += ((1 – costheta) * axis.x * axis.z – axis.y * sintheta) * p.x;
q.z += ((1 – costheta) * axis.y * axis.z + axis.x * sintheta) * p.y;
q.z += (costheta + (1 – costheta) * axis.z * axis.z) * p.z;
return q;
}
Composing Transformation
// white cube at origin
cube = GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType.Cube);
cube.GetComponent().material.color = new Color(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
cube.transform.parent = this.gameObject.transform;
// translation, rotation, scale
Vector3 translation = new Vector3(1.5, 0, 0);
Quaternion rotation = Quaternion.Euler(0, 0, 45);
Vector3 scale = new Vector3(0.2, 0.2, 0.2);
// white cube with S->R->T
cube.transform.localScale = scale;
cube.transform.rotation = rotation;
cube.transform.position = translation;
Matrix4x4 matrix = cube.transform.localToWorldMatrix;
Debug.Log(“cube.transform.localToWorldMatrix=\n” + matrix);
// Create a composing transformation Scale -> Rotation -> Translation
Matrix4x4 m1 = Matrix4x4.TRS(translation, rotation, scale);
// Create a composing transformation Scale -> Rotation -> Translation
Matrix4x4 m2 = Matrix4x4.Translate(translation) *
Matrix4x4.Rotate(rotation) * Matrix4x4.Scale(scale); // Scale -> Rotation -> Translation
if (m1 == m2) Debug.Log(“m1 == m2”);
if (m1 == matrix) Debug.Log(“m1 == matrix”);
// Create a composing transformation Translation -> Rotation ->Scale
Matrix4x4 m3 = Matrix4x4.Scale(scale) *
Matrix4x4.Rotate(rotation) * Matrix4x4.Translate(translation);
if (m1 != m3) Debug.Log(“m1 != m3”);
Unity Transformation
transform.position = new Vector3 (10, 0, 0); // 현재 transform 컴포넌트의 position 값을 위치 (10, 0, 0)로 이동한다
transform.localPosition = new Vector3 (10, 0, 0); // 부모 position의 상대적인 위치로 (10, 0, 0) 이동한다
transform.Translate (10, 0, 0); // 현재 position에서 (10, 0, 0) 만큼 이동한다.
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Euler (new Vector3 (10, 0, 0)); // 현재 transform 컴포넌트의 rotation 값을 오일러각 (10, 0, 0) 로 회전한다.
transform.Rotate (10, 0, 0); // 현재 rotation에서 (10, 0, 0)만큼 회전한다.
transform.localScale = new Vector3 (10, 10, 10); // transform 컴포넌트의 scale 값을 (10, 10, 10) 으로 크기변환한다.
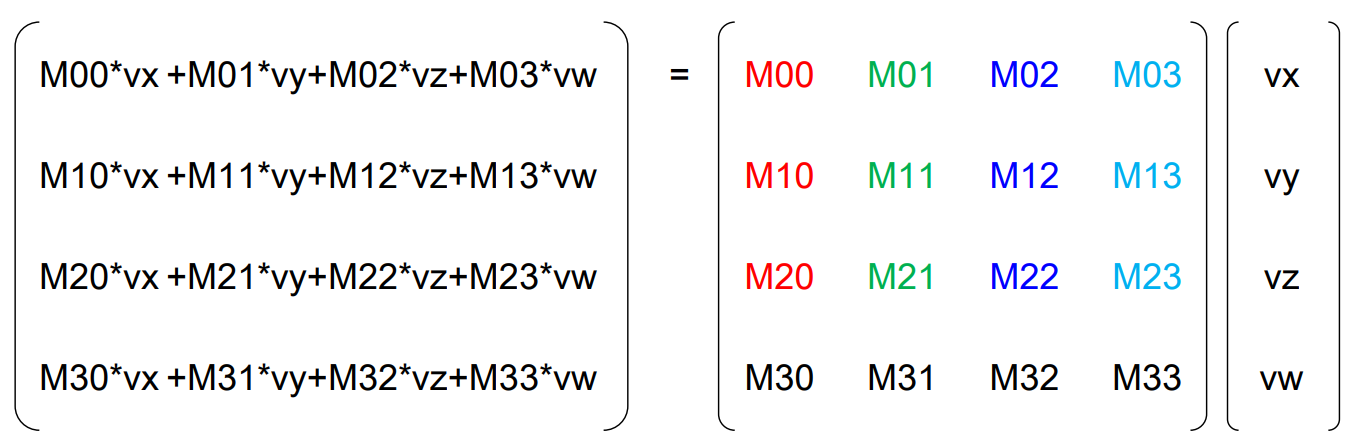
Unity Matrix (Column-Major Order)
Vector3 Position = new Vector3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
Matrix4x4 Model = Matrix4x4.Translate(new Vector3(1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f));
// Debug.Log(Model);
// (1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
// (0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 2.0)
// (0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 3.0)
// (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
Vector3 Transformed = Model.MultiplyPoint3x4(Position); // P’ (1, 2, 3) (Unity Matrix uses Column-Major Order)