Identifier – naming conventions
Variables – local vs class variable, instance vs static variable
Data Type – primitive vs reference data type
Type Conversion – implicit vs explicit type conversion, int <-> String conversion, numeric data type conversion
Operator – arithmetic vs relational vs bitwise vs logical vs assignment operator, operator precedence, postfix vs prefix increment/decrement operator
Control Statement – if/else, switch, for/foreach, while/do-while, break/continue
Array – primitive vs object array, 2D array, returning an array vs passing an array as parameter
Enum – enum data type, enum Operation example, enum Operator, enum Gender
Method – parameter passing (pass-by value – primitive vs reference data type), swap, method overloading vs overriding
OOP(Encapsulation, Inheritance, Polymorphism)
Class – default/public/protected/private, instance vs static member, constructor usage guideline, singleton design pattern vs static class,
Inheritance – BankAccount SavingAccount CheckingAccount class(instance vs static member), Car Sedan class (default/public/protected/private), Person Student class (instance vs static method overriding)
Polymorphism – Polymorphism vs Method Overriding vs Method Overloading, Abstract Class & Polymorphism
Interface – Comparable & Comparator Interface, Shape Polymorphism with Interface
Swing – Swing Component, Layout Manager, 5 Ways to Implement Event Listener, Event Listener (ChangeListener, KeyListener, ActionListener), TemperatureConverter, MetricConverter, AridityIndex, BMICalculator, Key Mouse Motion Listener & Adapter, Custom Component, TripleCalculatorFrame
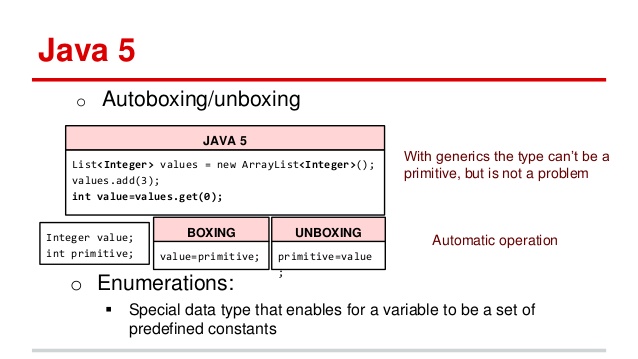
Collections – autoboxing and unboxing, Array vs ArrayList,
Difference between Array and ArrayList,
Equals vs Contains, == vs equals vs hashCode