import java.util.*;
class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
private static int count = 0; // static (class) field
protected String name; // instance field
protected int age; // instance field
public Person() {
//System.out.println("Person Constructor"); // this("", 0); error: call to this must be first statemenht in constructor
this("", 0);
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
count++;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person(Person other) {
this(other.name, other.age);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void set(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void set(Person other) {
this.name = other.name;
this.age = other.age;
}
public Person clone() {
Person p = new Person(this.name, this.age);
return p;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) { // Object.equals overriding
if (other instanceof Person) {
Person that = (Person) other;
return that.canEqual(this) && this.getName().equals(that.getName()) && this.getAge() == that.getAge();
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return (41 * getName().hashCode() + getAge());
}
public boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return (other instanceof Person);
}
@Override
public String toString() { // Object.toString() overriding
return "Person Name: " + name + " Age: " + age;
}
public void print() { // instance methods
System.out.println("Person Name: " + name + " Age: " + age);
}
public static void printCount() { // static (class) methods
System.out.println("Person Count: " + count);
}
public static int getCount() { // static (class) methods
return count;
}
public static void setCount(int value) { // static (class) methods
count = value;
}
public int compareTo(Person other) {
String thisName = this.getName().toUpperCase();
String otherName = ((Person)other).getName().toUpperCase();
//ascending order
return thisName.compareTo(otherName);
//descending order
//return otherName.compareTo(thisName);
}
public static Comparator<Person> AgeComparator = new Comparator<Person>() {
public int compare(Person p1, Person p2) {
int age1 = p1.getAge();
int age2 = p2.getAge();
//ascending order
return age1 – age2;
//descending order
//return age2 – age1;
}
};
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class Student extends Person {
private static int count = 0; // static (class) field
protected int id;
public Student() {
id = 5208;
}
public Student(String name, int age, int id) {
super(name, age);
this.id = id;
count++;
}
public int getID() {
return id;
}
public void setID(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void set(String name, int age, int id) {
super.set(name, age);
this.id = id;
}
public void set(String name, int age) {
super.set(name, age);
}
public void set(Student other) {
this.set(other.name, other.age, other.id);
}
public void set(Person other) {
if (other instanceof Person)
super.set(other);
else
this.set((Student)other);
}
public Student clone() {
Student s = new Student(this.name, this.age, this.id);
return s;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) { // Object.equals overriding
if (other instanceof Student) {
Student that = (Student) other;
return that.canEqual(this) && this.getName().equals(that.getName()) && this.getAge() == that.getAge() && this.getID() == that.getID();
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return (41 * super.hashCode() + getID());
}
public boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return (other instanceof Student);
}
@Override
public String toString() { // Object.toString() overriding
return "Student Name: " + name + " Age: " + age + " ID: " + id;
}
public void superPrint() {
super.print();
}
public void print() { // Person.print() method overriding
System.out.println("Student Name: " + name + " Age: " + age + " ID: " + id);
}
public static void printCount() { // static (class) methods
System.out.println("Student Count: " + count);
}
public static int getCount() { // static (class) methods
return count;
}
public static void setCount(int value) { // static (class) methods
count = value;
}
public int compareTo(Student other) {
String thisName = this.getName().toUpperCase();
String otherName = ((Student)other).getName().toUpperCase();
//ascending order
return thisName.compareTo(otherName);
//descending order
//return otherName.compareTo(thisName);
}
public static Comparator<Student> AgeComparator = new Comparator<Student>() {
public int compare(Student p1, Student p2) {
int age1 = p1.getAge();
int age2 = p2.getAge();
//ascending order
return age1 – age2;
//descending order
//return age2 – age1;
}
};
public static Comparator<Student> IDComparator = new Comparator<Student>() {
public int compare(Student p1, Student p2) {
int id1 = p1.getID();
int id2 = p2.getID();
//ascending order
return id1 – id2;
//descending order
//return id2 – id1;
}
};
}
class PersonStudentTest {
public static void print(Object[] array) {
for(Object o : array) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Person jason1 = new Person("Jason", 10);
Person jason2 = new Person("Jason", 10);
Person jason3 = jason1;
Person jason4 = new Person("Jason", 20);
if (jason1 == jason2)
System.out.println("jason1 == jason2");
else
System.out.println("jason1 != jason2"); // 동일한 reference를 가리키지 않으므로 jason1 != jason2
if (jason1 == jason3)
System.out.println("jason1 == jason3"); // 동일한 reference이므로 jason1 == jason3
else
System.out.println("jason1 != jason3");
if (jason1.equals(jason4))
System.out.println("jason1 == jason4");
else
System.out.println("jason1 != jason4"); // 동일한 reference를 가리키지 않으므로 jason1 != jason4
if (jason1.equals(jason2))
System.out.println("jason1 equals to jason2"); // 내용이 같으므로 jason1 equals to jason2
else
System.out.println("jason1 is not equal to jason2");
if (jason1.equals(jason3))
System.out.println("jason1 equals to jason3"); // 내용이 같으므로 jason1 equals to jason3
else
System.out.println("jason1 is not equal to jason3");
if (jason1.equals(jason4))
System.out.println("jason1 equals jason4");
else
System.out.println("jason1 is not equal to jason4"); // 내용이 다르므로 jason1 is not equal to jason4
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Student john1 = new Student("John", 10, 100);
Student john2 = new Student("John", 10, 100);
Student john3 = john1;
Student john4 = new Student("John", 20, 100);
if (john1.equals(john2))
System.out.println("john1 equals to john2"); // 내용이 같으므로 john1 equals to john2
else
System.out.println("john1 is not equal to john2");
if (john1.equals(john3))
System.out.println("john1 equals to john3"); // 내용이 같으므로 john1 equals to john3
else
System.out.println("john1 is not equal to john3");
if (john1.equals(john4))
System.out.println("john1 equals to john4");
else
System.out.println("john1 is not equal to john4"); // 내용이 다르므로 john1 is not equal to john4
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Student[] sList = new Student[3];
sList[0] = new Student("Kevin", 0, 222);
sList[1] = new Student("Jason", 1, 333);
sList[2] = new Student("John", 2, 111);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT BY NAME (DEFAULT)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList);
print(sList);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by AGE!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList, Student.AgeComparator);
print(sList);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by ID!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList, Student.IDComparator);
print(sList);
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Student[] sList2 = new Student[3];
sList2[0] = new Student("Kevin", 0, 222);
sList2[1] = new Student("Jason", 1, 333);
sList2[2] = new Student("John", 2, 111);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT BY NAME (anonymous method)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList2, new Comparator<Student>() {
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
return s1.getName().toUpperCase().compareTo(s2.getName().toUpperCase());
}
});
print(sList2);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by AGE (anonymous method)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList2, new Comparator<Student>() {
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
return s1.getAge() – s2.getAge();
}
});
print(sList2);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by ID (anonymous method)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList2, new Comparator<Student>() {
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
return s1.getID() – s2.getID();
}
});
print(sList2);
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Student[] sList3 = sList2;
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT BY NAME (lambda)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList3, (Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
ss1.getName().compareTo(ss2.getName())
);
Arrays.stream(sList3).forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by AGE (lambda)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList3, (Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
Integer.compare(ss1.getAge(), ss2.getAge())
);
Arrays.stream(sList3).forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by ID (lambda)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList3, (Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
Integer.compare(ss1.getID(), ss2.getID())
);
Arrays.stream(sList3).forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
List<Student> sList4 = new ArrayList<Student>();
sList4.add(new Student("Kevin", 0, 222));
sList4.add(new Student("Jason", 1, 333));
sList4.add(new Student("John", 2, 111));
System.out.println("STUDENTLIST SORT BY NAME (lambda)!!!");
sList4.sort((Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
ss1.getName().compareTo(ss2.getName())
);
sList4.forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
System.out.println("STUDENTLIST SORT by AGE (lambda)!!!");
sList4.sort((Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
ss1.getAge() – ss2.getAge()
);
sList4.forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
System.out.println("STUDENTLIST SORT by ID (lambda)!!!");
sList4.sort((Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
ss1.getID() – ss2.getID()
);
sList4.forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
}
}
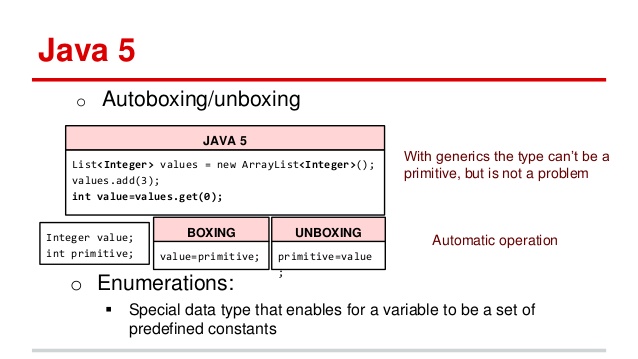
Autoboxing and Unboxing (Java1.5)
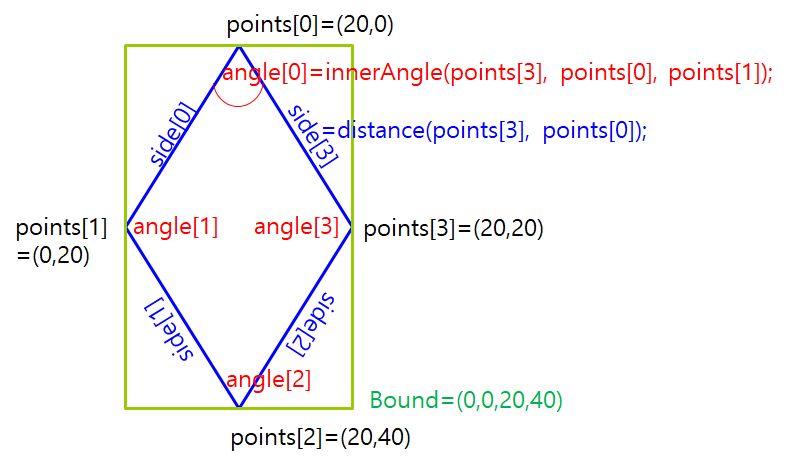
Figure
Figure – points, sides, angles, bound
Figure
private static final Point[] trianglePoints = { new Point(10, 0), new Point(0, 10), new Point(10, 10) };
private static final Point[] rectanglePoints = { new Point(0, 0), new Point(0, 20), new Point(30, 20), new Point(30, 0) };
private static final Point[] trapezoidPoints = { new Point(10, 0), new Point(0, 20), new Point(30, 20), new Point(20, 0) };
private static final Point[] squarePoints = { new Point(0, 0), new Point(0, 20), new Point(20, 20), new Point(20, 0) };
private static final Point[] parallelogramPoints = { new Point(10, 0), new Point(0, 20), new Point(20, 20), new Point(30, 0) };
private static final Point[] rhombusPoints = { new Point(10, 0), new Point(0, 20), new Point(10, 40), new Point(20, 20) };
private static final Point[] kitePoints = { new Point(10, 0), new Point(0, 10), new Point(10, 40), new Point(20, 10)};
FigureUML
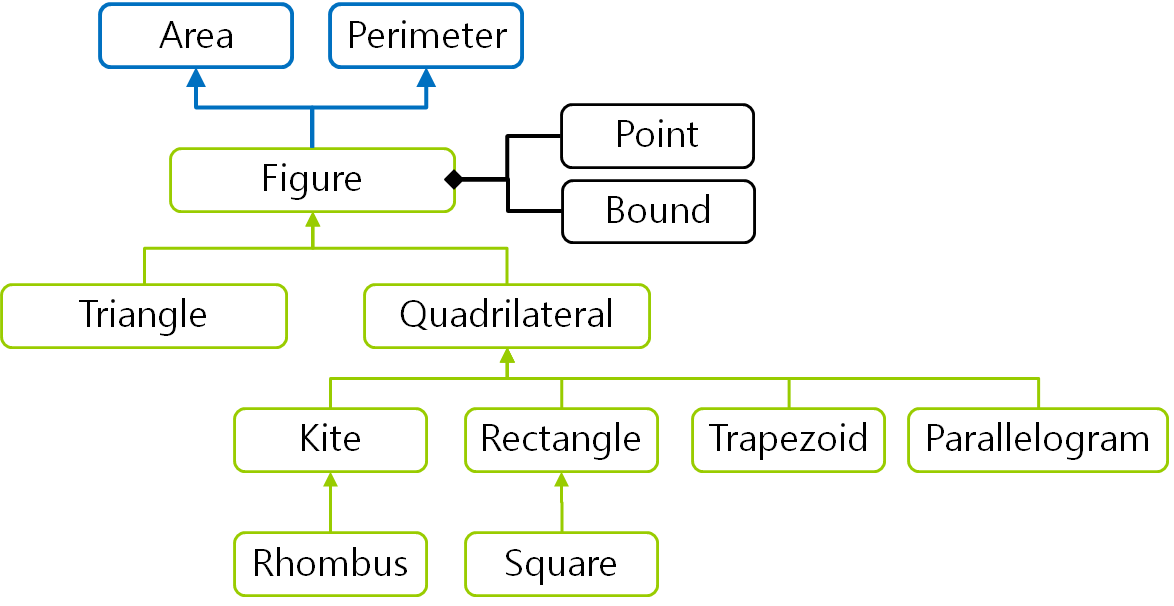
Figure has array of Point, array of sides, array of angles, a bound.
Figure setPoints updateSides, updateAngles, updateBound.
Figure updateSides calculates sides (using distance between two points).
Figure updateAngles calculates innerAngles (using innerAngle between two vectors).
Figure updateBound calculates bound (using findBound – xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax of points).
Triangle getAdditionalUserInput gets 3 Points and setPoints (triangle’s points, sides, angles, bound).
Quadrilateral getAdditionalUserInput gets 4 Points and setPoints (quadrilateral’s points, sides, angles, bound).
Triangle perimeter() = sides[0] + sides[1] + sides[2]
Triangle area() = sides[0] * sides[1] * Math.sin(Math.toRadians(angles[1])) / 2.0
Quadrilateral perimeter() = sides[0] + sides[1] + sides[2] + sides[3]
Trapezoid setPoints also update top, bottom, height
Trapezoid area() = (top + bottom) * height / 2.0
Kite setPoints also update diagonal1 & diagonal2
Kite area() = diagonal1 * diagonal2 / 2.0
Rhombus area() is the same as Kite area()
Rectangle area() = sides[0] * sides[1]
Square area() is the same as Rectangle area()
Distance between two points & Angle between two vectors
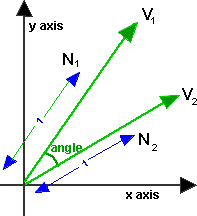
If v1 and v2 are normalised so that |v1|=|v2|=1, then angle = acos(v1•v2)
http://www.euclideanspace.com/maths/algebra/vectors/angleBetween/
// 두 점 간의 거리 구하기
public static double distance(Point p1, Point p2) {
return Math.sqrt((p2.getX() – p1.getX()) * (p2.getX() – p1.getX()) + (p2.getY() – p1.getY()) * (p2.getY() – p1.getY()));
}
// 벡터의 길이
public static double length(Point p) {
return Math.sqrt(p.getX() * p.getX() + p.getY() * p.getY());
}
// 두 벡터간의 내적(dot product)
public static double dot(Point p1, Point p2) {
return p1.getX() * p2.getX() + p1.getY() * p2.getY();
}
// 세 점으로부터 도형의 내각 구하기 = acos(dot(v1, v2) / |v1|*|v2|)
public static double innerAngle(Point p1, Point p2, Point p3) {
Point v1 = new Point(p1.getX() – p2.getX(), p1.getY() – p2.getY()); // v1 = p1 – p2
Point v2 = new Point(p3.getX() – p2.getX(), p3.getY() – p2.getY()); // v2 = p3 – p2
double len1 = length(v1);
double len2 = length(v2);
double dot = dot(v1, v2);
double radian = Math.acos(dot / len1 * len2);
double angle = Math.toDegrees(radian);
return angle;
}
Lab6
Lab6 프로젝트 디렉토리 안에 모든 파일(src/*.java & bin/*.class)와 보고서 (2~3장)를 넣고 Lab6_학번_이름.zip 압축한 후 e-learning(http://lms.dankook.ac.kr/index.jsp)으로 제출 (Due by 5/20 연장)
Lab6 interface & is-a vs has-a
본인이 작성한 Lab5 도형클래스에 Point 클래스와 Bound 클래스를 포함한다. 도형의 점을 입력하여 도형의 면적과 둘레를 계산한다.
보고서는 출력해서 수업시작 전에 제출한다.
java1-lab6 (updated)
Figure 클래스
lecture7
lecture7
java1-lecture7
Shape Polymorphism with Interface
Shape 추상클래스 has-a ShapeType, ShapeColor, ShapeRect
Shape 추상클래스를 상속받은 Triangle, Rectangle, Square, Circle 클래스는 추상메소드인 void area()를 반드시 구현하였다.
Shape 추상클래스는 Moveable, Scalable 인터페이스를 상속하여 추상메소드인 Moveable 인터페이스의 void move(int, int)와 Scalable 인터페이스의 void scale(int)를 구현하였다.