lecture9
Managing Java Projects in VS Code
HW5 (due by 6/5)
HW5 (due by 6/5)
String + operator vs concat method
The + operator produces a new String by appending the second operand onto the end of the first operand.
Strings are NOT changed by the action of concat(). A new String is constructed that contains the character “Red Rose”.

How to Concatenate Strings in Java | Developer.com
Strings and Object References in Java: The concat() Method | Saylor Academy
lecture8
lecture8
HW4 (due by 5/22)
HW4 (due by 5/22)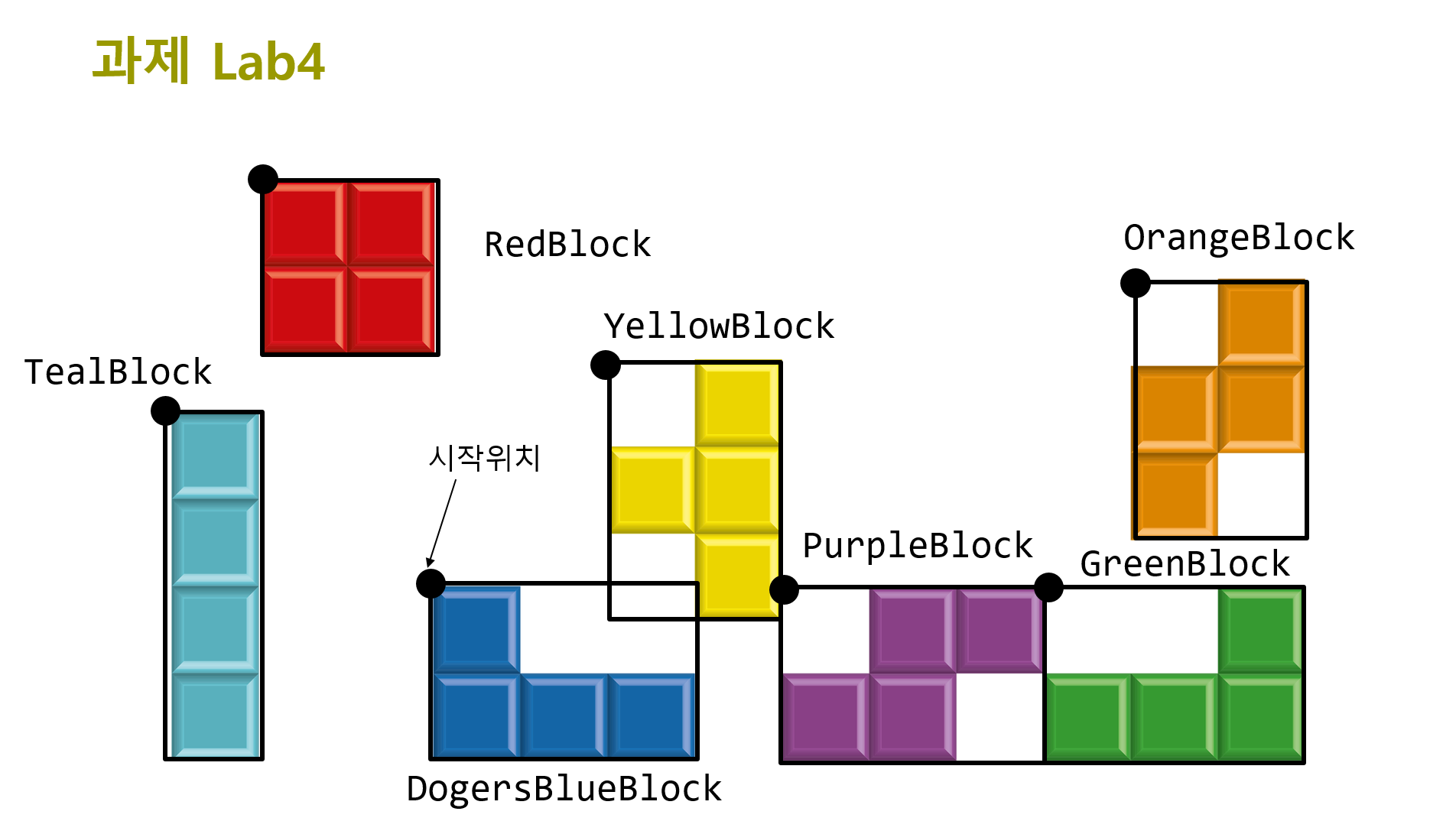
Java Double Colon Operator
Java :: 연산자 (Double Colon Operator)는 람다식을 대체하여 메서드 참조(method reference)로 사용된다. 즉, 람다식이 사용될 수 있는 Functional Interface Implementation에서만 사용 가능하다.
-
- Using Lambda
Comparator<Person> c = (Person p1, Person p2) -> p1.getName().compareTo(p2.getName());
- Using Lambda
-
- Using Lambda with type interference
Comparator<Person> c = (p1, p2) -> p1.getName().CompareTo(p2.getName()); - Using method reference ( :: operator)
Comparator<Person> c = Comparator.comparing(Person::getName); - Method reference ( :: operator)
Function<Person, String> getName = Person::getName; // Person->String String name = getName.apply(person1); - Method reference ( :: operator)는 람다식과 동일한 처리를 하는 식이지만 메소드 본문을 제공하는 대신 기존 메소드를 이름으로 참조한다.
Function<Double, Double> sq = (Double x) -> x * x; // lambda double result = sq.apply(3); // 3 * 3 = 9 Function<Double, Double> sq2 = MyClass::square; // MyClass에 정의된 square 정적 메소드 double result2 = sq2.apply(3); // 3 * 3 = 9
BiFunction<Double, Double, Double> add = (x, y) -> x + y; // lambda double result = add.apply(3.1, 3.2); // 3.1 + 3.2 = 6.3 BiFunction<Double, Double, Double> add2 = MyClass::sum; // MyClass에 정의된 sum 정적 메소드 double result2 = add2.apply(3.1, 3.2); // 3.1 + 3.2 = 6.3
- Using Lambda with type interference
Java Lambda Default Functional Interface
Java Lambda 기본 함수형 인터페이스 java.util.function 패키지에 정의되어 있음.
-
- Functions
public interface Function<T, R> { R apply(T t); }
- Functions
-
- Suppliers
public interface Supplier<T> { T get(); }
- Consumers
public interface Consumer<T> { void accept(T t); }
- Predicates
public interface Predicate<T> { boolean test(T t); }
- Operators
public interface UnaryOperator<T> extends Function<T, T> { static <T> UnaryOperator<T> identity() { return t -> t; } }
public interface BinaryOperator<T> extends BiFunction<T,T,T> { public static <T> BinaryOperator<T> minBy(Comparator<? super T> comparator) { Objects.requireNonNull(comparator); return (a, b) -> comparator.compare(a, b) <= 0 ? a : b; } public static <T> BinaryOperator<T> maxBy(Comparator<? super T> comparator) { Objects.requireNonNull(comparator); return (a, b) -> comparator.compare(a, b) >= 0 ? a : b; } }
- Suppliers
Comparable & Comparator Interface
import java.util.*;
class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
private static int count = 0; // static (class) field
protected String name; // instance field
protected int age; // instance field
public Person() {
//System.out.println("Person Constructor"); // this("", 0); error: call to this must be first statemenht in constructor
this("", 0);
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
count++;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person(Person other) {
this(other.name, other.age);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void set(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void set(Person other) {
this.name = other.name;
this.age = other.age;
}
public Person clone() {
Person p = new Person(this.name, this.age);
return p;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) { // Object.equals overriding
if (other instanceof Person) {
Person that = (Person) other;
return that.canEqual(this) && this.getName().equals(that.getName()) && this.getAge() == that.getAge();
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return (41 * getName().hashCode() + getAge());
}
public boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return (other instanceof Person);
}
@Override
public String toString() { // Object.toString() overriding
return "Person Name: " + name + " Age: " + age;
}
public void print() { // instance methods
System.out.println("Person Name: " + name + " Age: " + age);
}
public static void printCount() { // static (class) methods
System.out.println("Person Count: " + count);
}
public static int getCount() { // static (class) methods
return count;
}
public static void setCount(int value) { // static (class) methods
count = value;
}
public int compareTo(Person other) {
String thisName = this.getName().toUpperCase();
String otherName = ((Person)other).getName().toUpperCase();
//ascending order
return thisName.compareTo(otherName);
//descending order
//return otherName.compareTo(thisName);
}
public static Comparator<Person> AgeComparator = new Comparator<Person>() {
public int compare(Person p1, Person p2) {
int age1 = p1.getAge();
int age2 = p2.getAge();
//ascending order
return age1 – age2;
//descending order
//return age2 – age1;
}
};
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class Student extends Person {
private static int count = 0; // static (class) field
protected int id;
public Student() {
id = 5208;
}
public Student(String name, int age, int id) {
super(name, age);
this.id = id;
count++;
}
public int getID() {
return id;
}
public void setID(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void set(String name, int age, int id) {
super.set(name, age);
this.id = id;
}
public void set(String name, int age) {
super.set(name, age);
}
public void set(Student other) {
this.set(other.name, other.age, other.id);
}
public void set(Person other) {
if (other instanceof Person)
super.set(other);
else
this.set((Student)other);
}
public Student clone() {
Student s = new Student(this.name, this.age, this.id);
return s;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) { // Object.equals overriding
if (other instanceof Student) {
Student that = (Student) other;
return that.canEqual(this) && this.getName().equals(that.getName()) && this.getAge() == that.getAge() && this.getID() == that.getID();
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return (41 * super.hashCode() + getID());
}
public boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return (other instanceof Student);
}
@Override
public String toString() { // Object.toString() overriding
return "Student Name: " + name + " Age: " + age + " ID: " + id;
}
public void superPrint() {
super.print();
}
public void print() { // Person.print() method overriding
System.out.println("Student Name: " + name + " Age: " + age + " ID: " + id);
}
public static void printCount() { // static (class) methods
System.out.println("Student Count: " + count);
}
public static int getCount() { // static (class) methods
return count;
}
public static void setCount(int value) { // static (class) methods
count = value;
}
public int compareTo(Student other) {
String thisName = this.getName().toUpperCase();
String otherName = ((Student)other).getName().toUpperCase();
//ascending order
return thisName.compareTo(otherName);
//descending order
//return otherName.compareTo(thisName);
}
public static Comparator<Student> AgeComparator = new Comparator<Student>() {
public int compare(Student p1, Student p2) {
int age1 = p1.getAge();
int age2 = p2.getAge();
//ascending order
return age1 – age2;
//descending order
//return age2 – age1;
}
};
public static Comparator<Student> IDComparator = new Comparator<Student>() {
public int compare(Student p1, Student p2) {
int id1 = p1.getID();
int id2 = p2.getID();
//ascending order
return id1 – id2;
//descending order
//return id2 – id1;
}
};
}
class PersonStudentTest {
public static void print(Object[] array) {
for(Object o : array) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Student[] sList = new Student[3];
sList[0] = new Student("Kevin", 0, 222);
sList[1] = new Student("Jason", 1, 333);
sList[2] = new Student("John", 2, 111);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT BY NAME (DEFAULT)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList);
print(sList);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by AGE!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList, Student.AgeComparator);
print(sList);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by ID!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList, Student.IDComparator);
print(sList);
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Student[] sList2 = new Student[3];
sList2[0] = new Student("Kevin", 0, 222);
sList2[1] = new Student("Jason", 1, 333);
sList2[2] = new Student("John", 2, 111);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT BY NAME (anonymous method)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList2, new Comparator<Student>() {
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
return s1.getName().toUpperCase().compareTo(s2.getName().toUpperCase());
}
});
print(sList2);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by AGE (anonymous method)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList2, new Comparator<Student>() {
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
return s1.getAge() – s2.getAge();
}
});
print(sList2);
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by ID (anonymous method)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList2, new Comparator<Student>() {
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
return s1.getID() – s2.getID();
}
});
print(sList2);
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Student[] sList3 = sList2;
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT BY NAME (lambda)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList3, (Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
ss1.getName().compareTo(ss2.getName())
);
Arrays.stream(sList3).forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by AGE (lambda)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList3, (Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
Integer.compare(ss1.getAge(), ss2.getAge())
);
Arrays.stream(sList3).forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
System.out.println("STUDENT SORT by ID (lambda)!!!");
Arrays.sort(sList3, (Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
Integer.compare(ss1.getID(), ss2.getID())
);
Arrays.stream(sList3).forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
List<Student> sList4 = new ArrayList<Student>();
sList4.add(new Student("Kevin", 0, 222));
sList4.add(new Student("Jason", 1, 333));
sList4.add(new Student("John", 2, 111));
System.out.println("STUDENTLIST SORT BY NAME (lambda)!!!");
sList4.sort((Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
ss1.getName().compareTo(ss2.getName())
);
sList4.forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
System.out.println("STUDENTLIST SORT by AGE (lambda)!!!");
sList4.sort((Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
ss1.getAge() – ss2.getAge()
);
sList4.forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
System.out.println("STUDENTLIST SORT by ID (lambda)!!!");
sList4.sort((Student ss1, Student ss2) ->
ss1.getID() – ss2.getID()
);
sList4.forEach((s) -> System.out.println(s));
}
}
Shape Polymorphism with Interface
Shape 추상클래스 has-a ShapeType, ShapeColor, ShapeRect
Shape 추상클래스를 상속받은 Triangle, Rectangle, Square, Circle 클래스는 추상메소드인 void area(), void perimeter()를 반드시 구현하였다.
Shape 추상클래스는 Moveable, Scalable 인터페이스를 상속하여 추상메소드인 Moveable 인터페이스의 void move(int, int)와 Scalable 인터페이스의 void scale(int)를 구현하였다.
